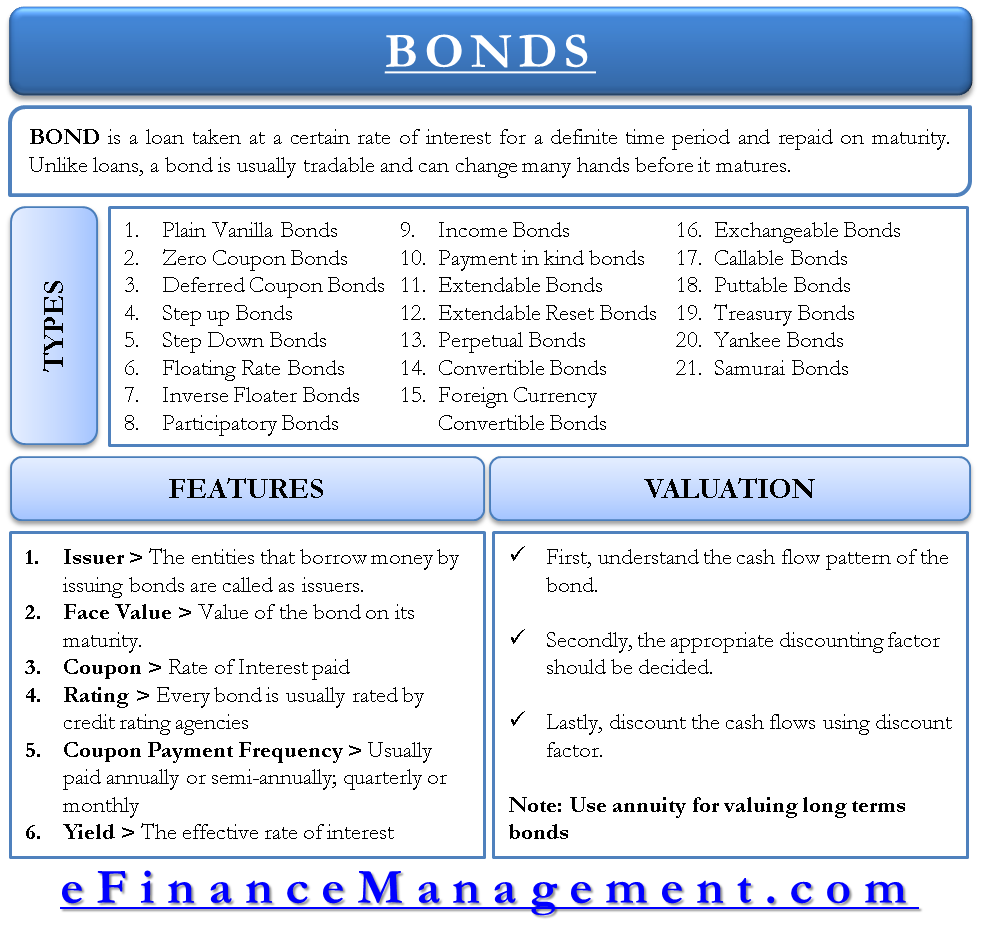
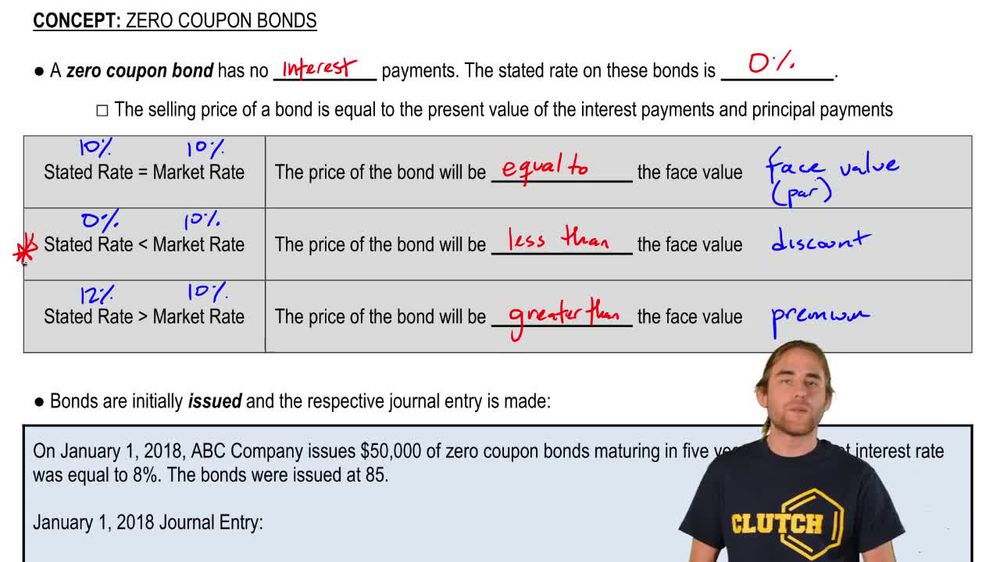
39 coupon vs zero coupon bonds
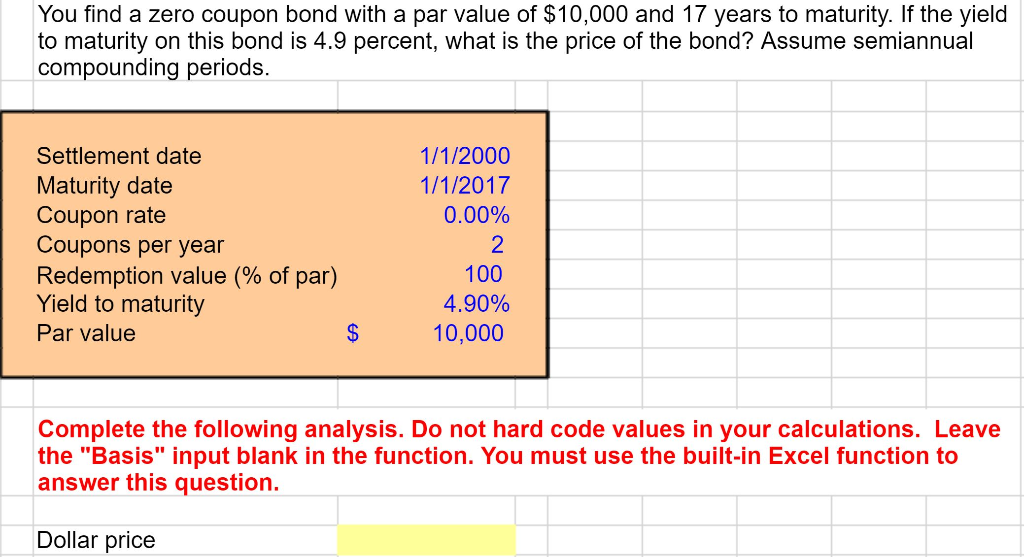
Zero Coupon Bond - (Definition, Formula, Examples, Calculations) = $463.19. Thus, the Present Value of Zero Coupon Bond with a Yield to maturity of 8% and maturing in 10 years is $463.19. The difference between the current price of the bond, i.e., $463.19, and its Face Value, i.e., $1000, is the amount of compound interest Compound Interest Compound interest is the interest charged on the sum of the principal amount and the total interest amassed on it so far. Coupon Bond Vs. Zero Coupon Bond: What's the Difference? Aug 31, 2020 · Zero-coupon bonds may also appeal to investors looking to pass on wealth to their heirs. If a bond selling for $2,000 is received as a gift, it only uses $2,000 of the yearly gift tax exclusion ...
Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Jan 31, 2022 · Zero-coupon bonds are also appealing for investors who wish to pass wealth on to their heirs but are concerned about income taxes or gift taxes. If a zero-coupon bond is purchased for $1,000 and ...

Coupon vs zero coupon bonds
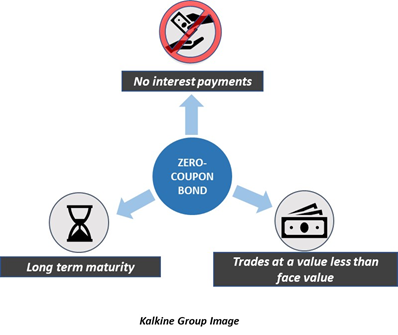
Zero-Coupon Bonds: Characteristics and Calculation Example Zero-coupon bonds are often perceived as long-term investments, although one of the most common examples is a “T-Bill,” a short-term investment. U.S. Treasury Bills (or T-Bills) are short-term zero-coupon bonds (< 1 year) issued by the U.S. government. Learn More → Zero Coupon Bond (SEC) Zero-Coupon Bond Price Formula Bond: Financial Meaning With Examples and How They Are Priced Jul 01, 2022 · Bond: A bond is a fixed income investment in which an investor loans money to an entity (typically corporate or governmental) which borrows the funds for a defined period of time at a variable or ... Individual bonds vs a bond fund - Bogleheads Jun 14, 2019 · If you need to satisfy date-certain future liabilities, a non-rolling ladder of individual bonds is superior to a bond fund. For example, if you commit to make a $10,000 a year payment to a charity for five years, the most effective way to invest for that is to buy 5 zero-coupon bonds, one maturing each year.
Coupon vs zero coupon bonds. What Is Coupon Rate and How Do You Calculate It? - SmartAsset Aug 26, 2022 · To calculate the bond coupon rate we add the total annual payments and then divide that by the bond’s par value: ($50 + $50) = $100; The bond’s coupon rate is 10%. This is the portion of its value that it repays investors every year. Bond Coupon Rate vs. Interest. Coupon rate could also be considered a bond’s interest rate. Individual bonds vs a bond fund - Bogleheads Jun 14, 2019 · If you need to satisfy date-certain future liabilities, a non-rolling ladder of individual bonds is superior to a bond fund. For example, if you commit to make a $10,000 a year payment to a charity for five years, the most effective way to invest for that is to buy 5 zero-coupon bonds, one maturing each year. Bond: Financial Meaning With Examples and How They Are Priced Jul 01, 2022 · Bond: A bond is a fixed income investment in which an investor loans money to an entity (typically corporate or governmental) which borrows the funds for a defined period of time at a variable or ... Zero-Coupon Bonds: Characteristics and Calculation Example Zero-coupon bonds are often perceived as long-term investments, although one of the most common examples is a “T-Bill,” a short-term investment. U.S. Treasury Bills (or T-Bills) are short-term zero-coupon bonds (< 1 year) issued by the U.S. government. Learn More → Zero Coupon Bond (SEC) Zero-Coupon Bond Price Formula















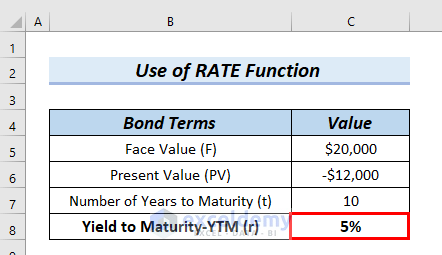





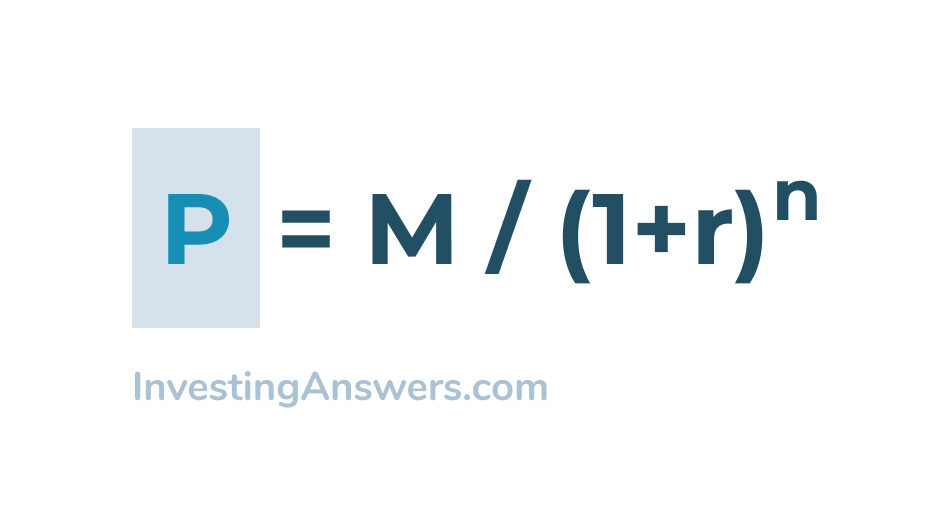
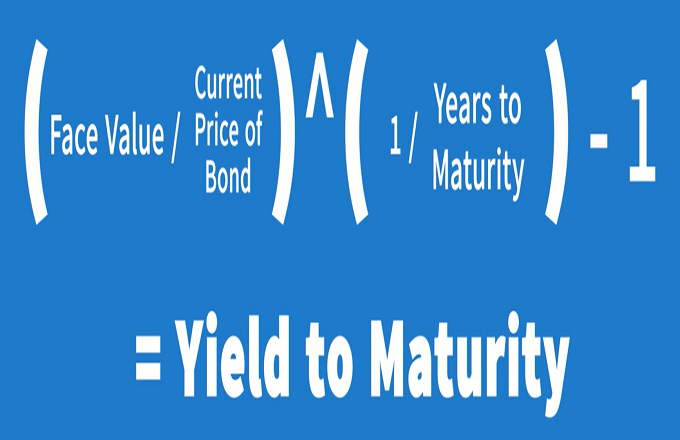

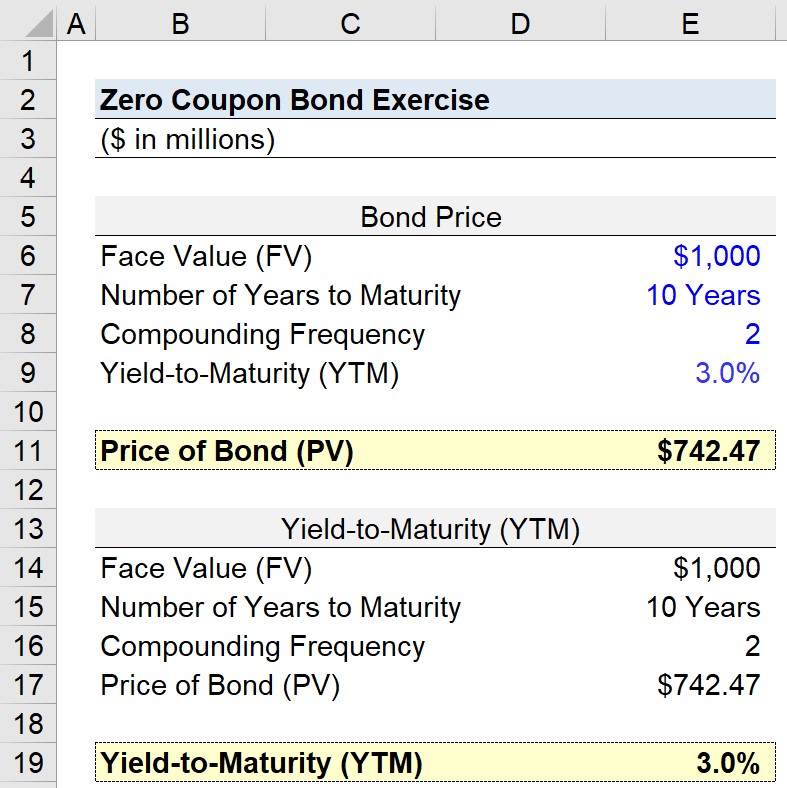


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/zero-couponbond_final-a6ec3618516a49c9a3654a1c79c9b681.png)
Post a Comment for "39 coupon vs zero coupon bonds"